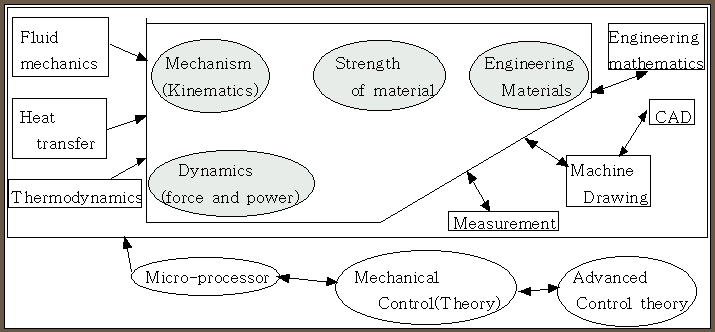
The forest of Mechanical Engineering)
MODERN CONTROL SYSTEMS
Chapter 1. Introduction to Control Systems
A control system consisting of interconnected components is designed to
achieve a desired purpose.
1.1 INTRODUCTION
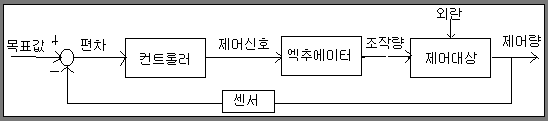
A control system is an interconnection of components forming a system
configuration that will provide a desired system response.

An open-loop control system utilizes an actuating device to control the
process directly without using feedback.
Open loop system :(manual)
Closed loop system(or Feedback loop system):(Automatic)
*Automation:
(without human being)
A closed-loop control system a measurement of the output and feedback
of this signal to compare it with the desired input(reference or command).
1.2 HISTORY OF AUTOMATIC CONTROL
-액체 높낮이 제어(Liquid level control)
B.C. 300년경 그리스 Ktesibios 물시계.
비잔틴 Philon 기름램프.
-증기압과 온도제어
증기압제어 - 1681년경 Denis Papin 안전밸브 발명.
온도제어 - 17세기경 네들란드 Cornelis Drebbel 달걀부화용 온도 제어 장치.
-속도제어
1745년 Edmud Lee 속도를 제어하기 위해 회전구 속도제어기(flyball speed
governor)를 발명.
-안정도, 안정화 및 조종
1868년 James Clerk Maxwell - 미분방정식의 계수에 근거한 3차 시스템의 안정도
판별법 발표.
1874년 Edward John Routh는 William Kingdom Clifford의 제안(Maxwell은 고려하지
않음)을 이용한 안정도 판별을 5차 시스템에 까지 확장.
1877년 Adams Prize의 주제 "The Criterion of Dynamical Stability" 이때 Routh는
"A Treatise on the Stability of a Given State of Motion"이란 제목의 논문을
제출하여 이상을 받음.
Alexandr Michailovich Lyapunov는 현대 제어시스템의 안정도이론 및 적용
방법에 대한 기초 확립.
-20세기 개발품
1922년 Sperry Gyroscope 주식회사는 적응제어와 보상원리를 이용한 자동조타시스템
개발.
오늘날 자동제어 시스템의 성능을 향상시키기 위해 이용되고 있는 이론의 대부분이
1855년 러시아에서 태어난 Nicholas Minorsky에 의해 제시.
오늘날 소위 비례-적분-미분 제어기(PID) 또는 3-모드 제어기(three-mode controller)
라고 불리는 제어방식으로 발전되어 배의 자동조타장치에 적용.
1920년대 후반과 1930년대 초반 - 벨연구소에 근무하던 H.W.Bode와 H.Nyquist는
피드백 증폭기의 해석법을 제시.(정현파 주파수 해석과 설계기법의 모태.)
1948년 항공산업에 종사하던 Walter R. Evans는 피드백시스템의 파라미터 변동에
따른 시스템의 특성방정식의 근궤적을 그리는 기법을 제시.
-현대의 응용
제어시스템은 미사일과 우주선뿐만 아니라 배와 비행기 등의 유도(guidance), 항해
(navigation) 및 제어 분야에서 널리 응용.
1.4 CONTROL ENGINEERING PRACTICE
Control engineering is concerned with the analysis and design of
goal-oriented system.
The control of an industrial process (manufacturing, production, and so
on) by automatic rather than manual means is often called automation.
Productivity is defined as the ratio of physical output to physical input.
1.5 EXAMPLES OF MODERN CONTROL SYSTEMS
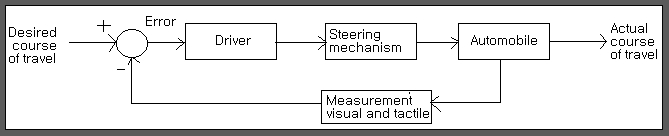
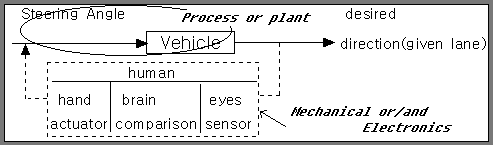
(a)Automobile steering control system.
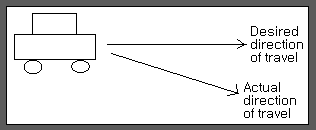
(b)The driver uses the difference between the actual and the desired direction of travel to generate a controlled adjustment of the steering wheel.

C)Typical direction of travel response
1.6 AUTOMATIC ASSEMBLY AND ROBOTS
Machines that automatically load and unload, cut, weld, or cast are used
by industry to obtain accuracy, safety, economy, and productivity.
1.7 THE FUTURE EVOLUTION OF CONTROL SYSTEMS
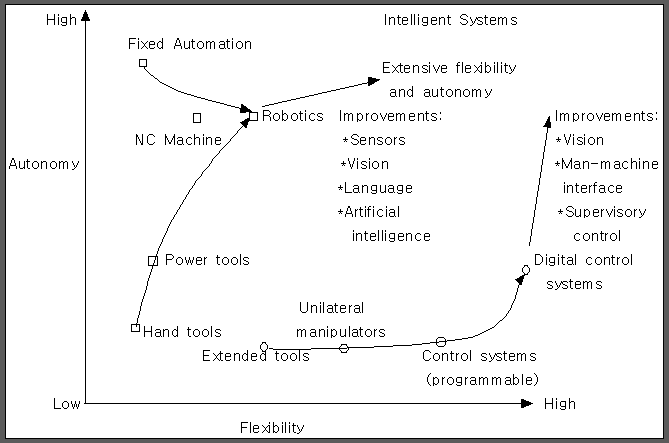
1.8 ENGINEERING DESIGN
Engineering design is the central task of the engineer. It is a complex
process in which both creativity and analysis play major roles.
Design is the process of conceiving or inventing the forms, parts, and
details of a system to achieve a specified purpose.
1.9 CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN
The design of control systems is a specific example of engineering design. Again, the goal of control engineering design is to obtain the configuration, specification, and identification of the key parameters of a proposed system to meet an actual need.
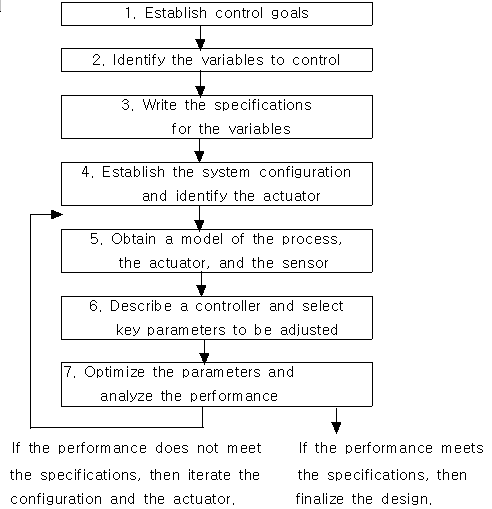
Figure1.19 The control system design process.
Real application example)
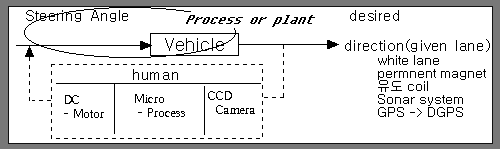
* ITS: Intellent Transportation System